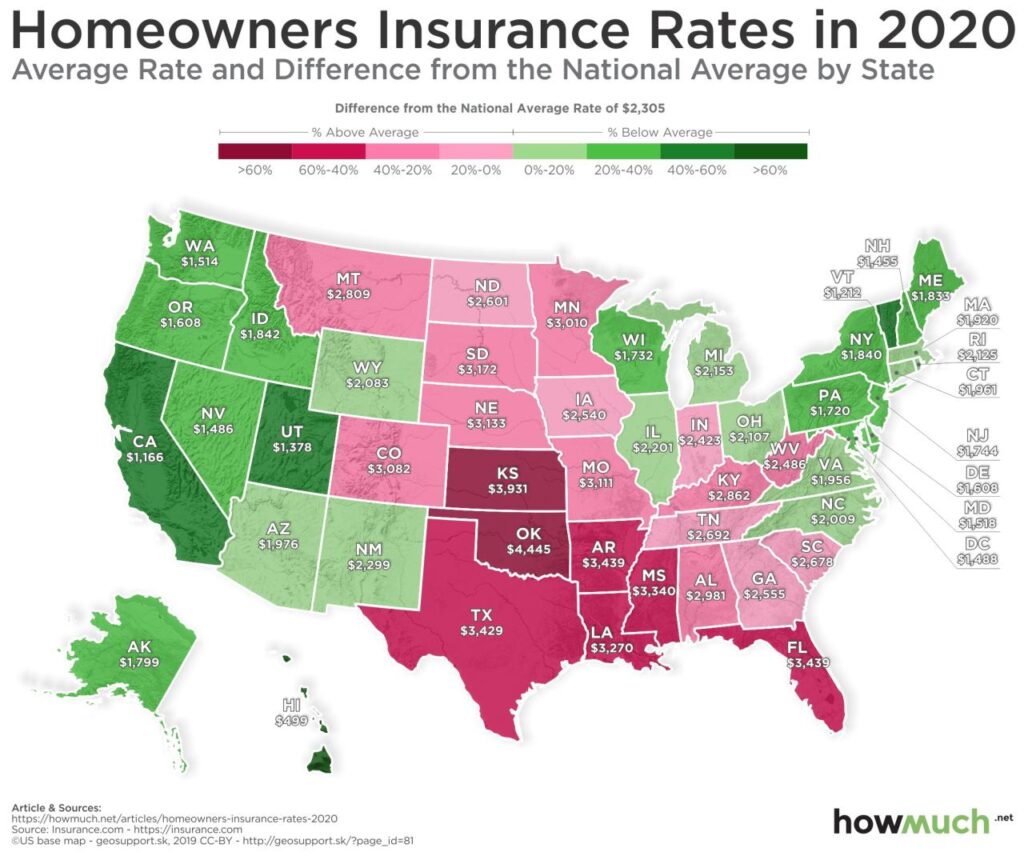
Homeowners insurance cost is a crucial aspect of homeownership, ensuring financial protection against unexpected events. This guide delves into the complexities of homeowners insurance, providing valuable insights into its components, factors influencing costs, and strategies for reducing premiums.
From understanding the fundamental aspects of coverage to navigating the insurance market, this comprehensive resource empowers homeowners to make informed decisions about their insurance needs.
Factors Influencing Homeowners Insurance Costs
Homeowners insurance premiums are influenced by a variety of factors that insurers use to assess the risk of insuring a particular property. These factors are carefully considered to ensure that premiums accurately reflect the likelihood of claims and the potential cost of covering those claims.
Location
The location of your home significantly impacts your homeowners insurance premiums. Insurers consider factors such as:
- Natural Disaster Risk: Areas prone to hurricanes, earthquakes, wildfires, or floods have higher premiums due to the increased likelihood of claims. For example, homes located in coastal areas with high hurricane risk will generally have higher premiums than homes in inland areas.
- Crime Rates: Areas with high crime rates have higher premiums because of the increased risk of theft and vandalism. For example, homes in neighborhoods with high burglary rates will likely have higher premiums than those in neighborhoods with low burglary rates.
- Proximity to Fire Stations and Hospitals: Homes located closer to fire stations and hospitals may have lower premiums as they are considered to have faster response times in case of emergencies. This can lead to lower potential damage costs.
Home Features
The features of your home also influence insurance costs. These features include:
- Age: Older homes tend to have higher premiums than newer homes due to factors like outdated wiring, plumbing, or roofing materials, which could increase the risk of claims. For example, a 100-year-old house with original wiring might have a higher premium than a 10-year-old house with updated wiring.
- Size: Larger homes generally have higher premiums than smaller homes because the potential cost of damage is higher. For example, a 5,000 square foot house would likely have a higher premium than a 2,000 square foot house.
- Construction Materials: Homes built with fire-resistant materials, such as brick or concrete, often have lower premiums than homes built with wood. For example, a brick home with a tile roof would generally have a lower premium than a wood-frame home with a shingle roof.
- Roof Type: Homes with newer and more durable roof materials, such as metal or slate, often have lower premiums than homes with older or more vulnerable roofing materials. For example, a home with a new metal roof would likely have a lower premium than a home with an old asphalt shingle roof.
- Security Systems: Homes with security systems, such as alarms or monitored surveillance, may qualify for discounts as they deter theft and vandalism. For example, a home with a professionally monitored security system might receive a discount on premiums.
Homeowner Risk Factors
Your individual risk factors as a homeowner also play a role in determining your insurance premiums. These factors include:
- Claims History: Homeowners with a history of filing claims, especially multiple claims, may have higher premiums. For example, a homeowner who has filed claims for water damage in the past might have a higher premium than a homeowner with no claims history.
- Credit Score: Your credit score can impact your homeowners insurance premiums. Insurers often use credit scores as a proxy for risk, assuming that those with good credit are more financially responsible and less likely to file claims. For example, a homeowner with a high credit score might receive a lower premium than a homeowner with a low credit score.
Insurance Coverage: Homeowners Insurance Cost
Homeowners insurance policies offer a comprehensive package of coverage designed to protect your home and belongings against various risks. Understanding the different types of coverage included in your policy is crucial for ensuring adequate protection and financial security.
Dwelling Coverage
Dwelling coverage is the most significant part of your homeowners insurance policy. It provides financial protection for your home’s structure, including the attached garage, permanent fixtures, and built-in appliances. This coverage protects you against damage caused by perils like fire, lightning, windstorms, hail, vandalism, and theft.
Personal Property Coverage, Homeowners insurance cost
Personal property coverage protects your belongings inside your home, such as furniture, electronics, clothing, and jewelry. It also covers personal property while it is away from your home, such as when you are on vacation. The amount of coverage you have for personal property is usually a percentage of your dwelling coverage, typically 50% to 70%.
Liability Coverage
Liability coverage protects you against financial losses resulting from accidents or injuries that occur on your property. This coverage helps pay for legal defense costs, medical expenses, and other damages that you may be responsible for. For example, if a visitor slips and falls on your icy driveway, your liability coverage would help pay for their medical bills and any legal expenses.
Additional Living Expenses
Additional living expenses coverage, also known as loss of use coverage, helps pay for temporary housing and other expenses if your home becomes uninhabitable due to a covered peril. This coverage can help you pay for hotel accommodations, meals, and other essential living expenses while your home is being repaired or rebuilt.
Homeowners Insurance
Understanding the nuances of homeowners insurance is crucial for protecting your most valuable asset – your home. While the basic principles remain the same, the specific factors influencing your premium can vary significantly depending on the type of home you own. This section delves into the unique considerations for different home types, offering insights into average costs, key influencing factors, and practical tips for potentially lowering your premiums.
Homeowners Insurance: Key Considerations for Different Home Types
The cost of homeowners insurance can vary greatly depending on the type of home you own. This table provides an overview of average costs, key factors influencing those costs, and tips for potentially lowering your premiums for different home types.
| Home Type | Average Cost | Key Factors Affecting Cost | Tips for Lowering Costs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Family Home | $1,500 – $2,500 per year |
|
|
| Condominium | $500 – $1,000 per year |
|
|
| Townhouse | $1,000 – $2,000 per year |
|
|
| Manufactured Home | $500 – $1,500 per year |
|
|
Epilogue
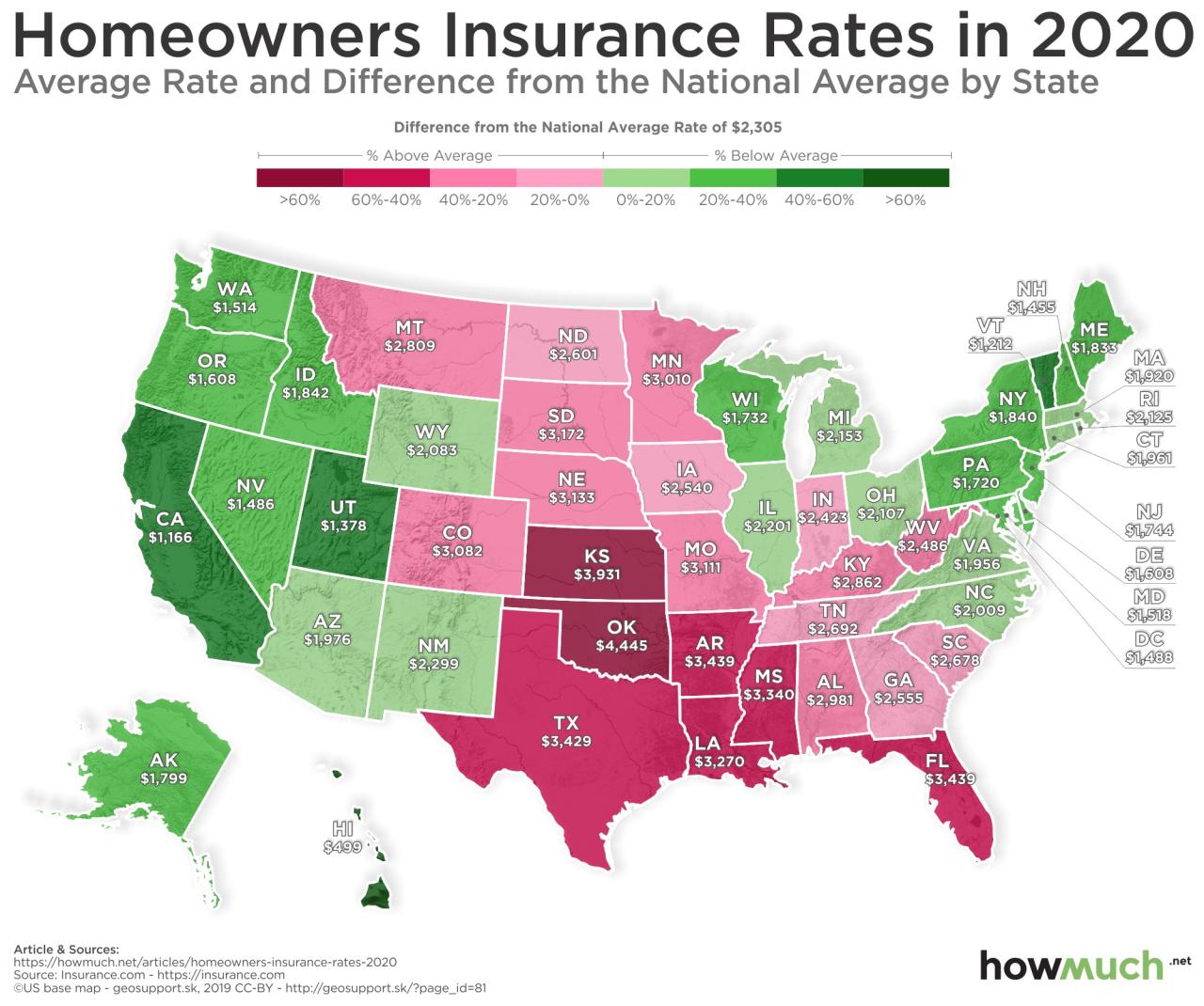
By understanding the intricacies of homeowners insurance, homeowners can confidently navigate the insurance market, secure adequate coverage, and protect their financial well-being. With a clear grasp of factors influencing costs, effective strategies for lowering premiums, and knowledge of the claims process, homeowners can ensure their investments are properly safeguarded.
Homeowners insurance costs can vary significantly based on factors like location, property value, and coverage levels. Just like homeowners insurance protects your dwelling, chip insurance safeguards your valuable electronic devices. Understanding the different types of coverage available for your home and your electronics can help you make informed decisions about your insurance needs.