Media liability insurance sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
In the dynamic world of media, where every word, image, and sound can have a profound impact, safeguarding your professional reputation and financial well-being is paramount. Media liability insurance acts as a vital shield, protecting media professionals from the myriad risks inherent in their work. From journalists and broadcasters to photographers and filmmakers, this insurance provides crucial coverage against potential claims arising from errors, omissions, defamation, copyright infringement, and other legal issues. It ensures that you have the financial resources to navigate legal challenges and mitigate potential financial losses, allowing you to focus on creating impactful content with peace of mind.
What is Media Liability Insurance?
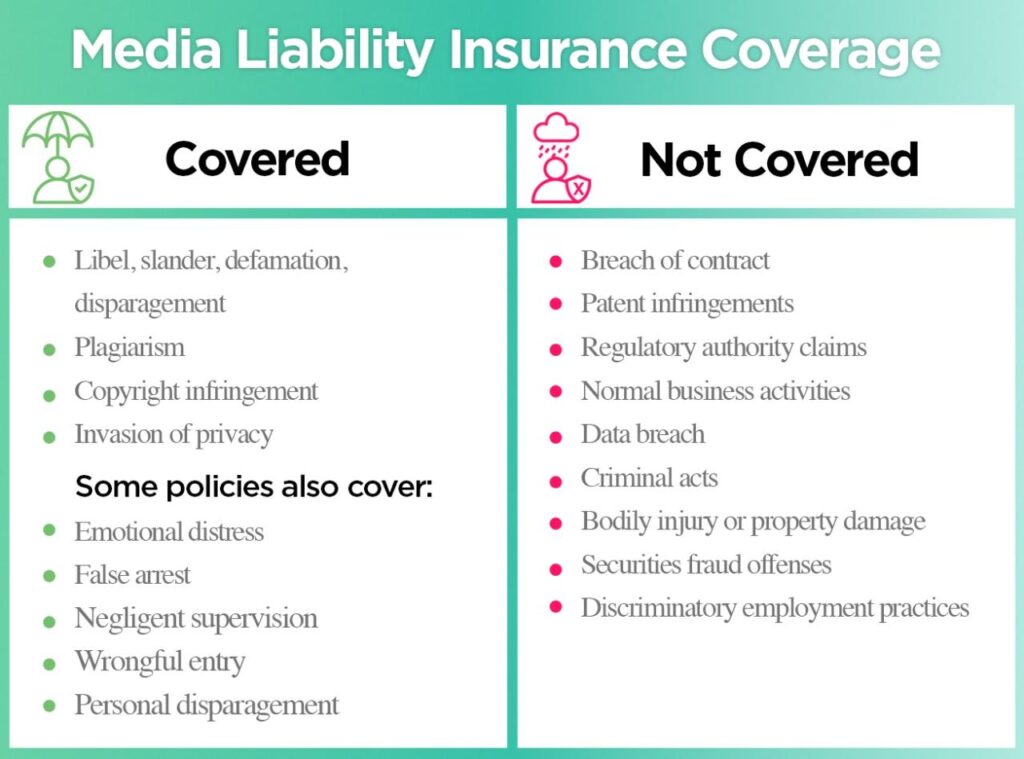
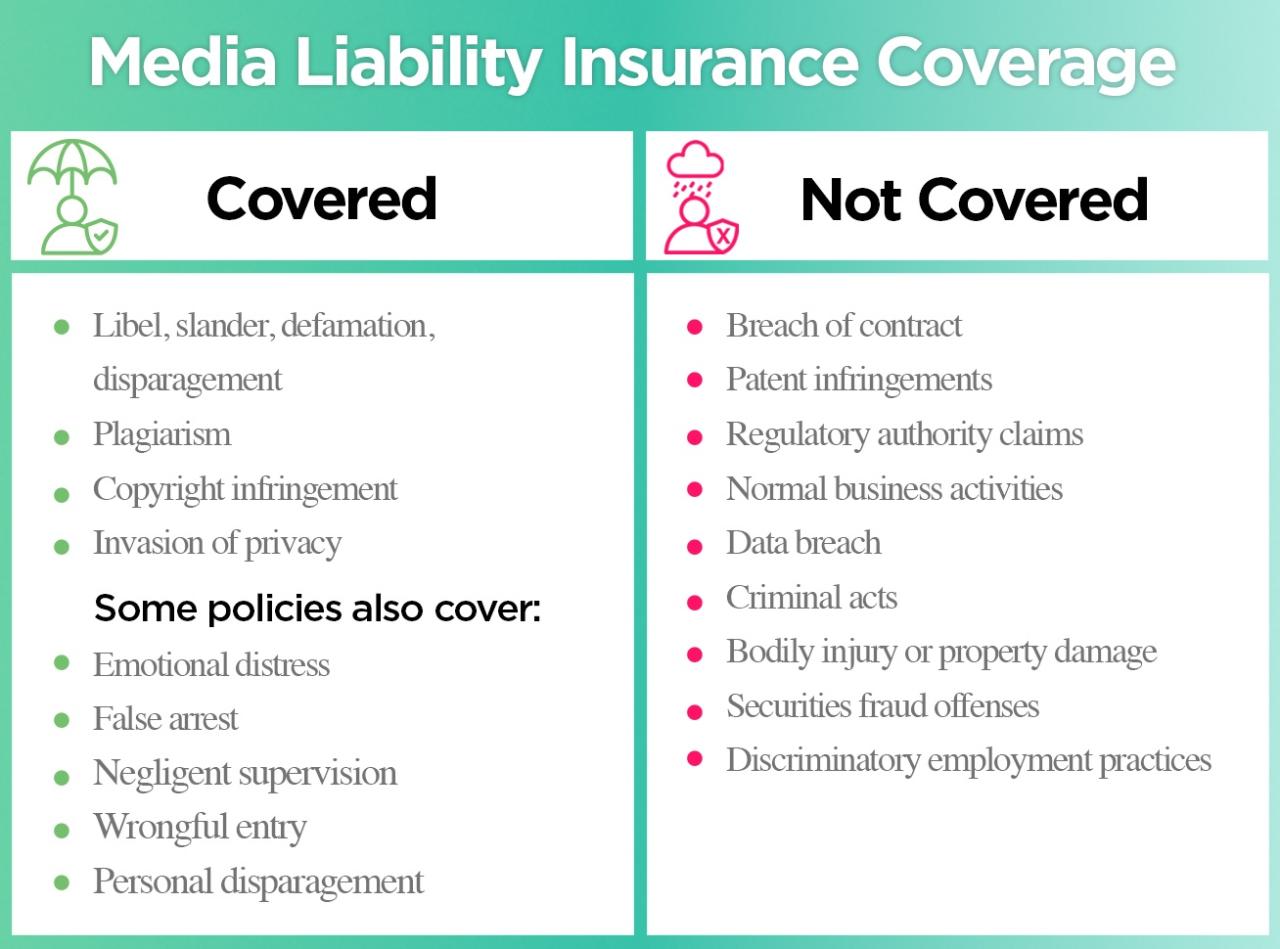
Media liability insurance is a type of insurance designed to protect media professionals from financial losses arising from claims related to their work. It provides coverage for legal defense costs, settlements, and judgments that may result from allegations of negligence, defamation, copyright infringement, or other legal issues.
Purpose and Scope of Media Liability Insurance
Media liability insurance aims to safeguard media professionals from the financial burden of lawsuits and other legal claims. It acts as a safety net, providing coverage for various risks associated with their work. The scope of this insurance typically encompasses:
- Defamation: This covers claims of libel (written) or slander (spoken) that damage an individual’s reputation. It protects media professionals from lawsuits stemming from false or misleading statements published or broadcasted.
- Copyright Infringement: This covers claims related to unauthorized use of copyrighted material, such as music, images, or text. It helps media professionals avoid legal repercussions for violating copyright laws.
- Privacy Violations: This covers claims arising from the unauthorized use or disclosure of private information, such as personal details or confidential communications.
- Negligence: This covers claims of carelessness or failure to exercise reasonable care in performing professional duties. For instance, it may cover claims related to errors in reporting or inaccurate information.
Media Professionals Who Need Media Liability Insurance
Media liability insurance is crucial for a wide range of media professionals, including:
- Journalists: Journalists are constantly gathering and reporting information, and they may face lawsuits for publishing false or misleading information.
- Photographers: Photographers may be sued for using images without permission or for invading someone’s privacy.
- Filmmakers: Filmmakers may face claims related to copyright infringement, defamation, or invasion of privacy, particularly when working on documentaries or biographical films.
- Bloggers and Social Media Influencers: Bloggers and influencers may be held liable for their online posts, particularly if they contain defamatory statements or infringe on copyrights.
- Publishers: Publishers, whether traditional or online, need media liability insurance to protect themselves from claims related to the content they publish.
- Public Relations Professionals: PR professionals may be sued for making false or misleading statements on behalf of their clients.
Risks Faced by Media Professionals
Media professionals face numerous risks in their day-to-day operations. These risks can result in costly lawsuits and legal battles, highlighting the importance of media liability insurance:
- False or Misleading Information: Errors in reporting, misinterpretations, or biased information can lead to defamation claims.
- Invasion of Privacy: Publishing private information without consent or using images without permission can lead to privacy violations.
- Copyright Infringement: Using copyrighted material without authorization can result in legal action from the copyright holder.
- Libel and Slander: Publishing or broadcasting false statements that damage an individual’s reputation can lead to defamation lawsuits.
- Negligence in Reporting: Failure to exercise reasonable care in gathering and verifying information can result in claims of negligence.
Key Coverage Components
Media liability insurance policies offer various coverage components to protect media professionals and organizations from financial risks associated with their work. Understanding these components is crucial for choosing the right policy and ensuring adequate protection.
Coverage for Libel and Slander
Libel and slander are forms of defamation that can significantly damage a person’s reputation and lead to legal action. This coverage component protects against financial losses arising from lawsuits alleging libel or slander.
- Libel is written defamation, while slander is spoken defamation.
- Both libel and slander require proof of:
- A false statement about a person
- Publication of the statement to a third party
- Damage to the person’s reputation
- Examples of scenarios where this coverage would be activated include:
- A journalist publishes an article containing false information about a politician, leading to a libel lawsuit.
- A radio host makes defamatory remarks about a business owner during a live broadcast, resulting in a slander lawsuit.
Coverage for Invasion of Privacy
Invasion of privacy occurs when someone intrudes upon another person’s private life without their consent. This coverage component protects against financial losses arising from lawsuits alleging invasion of privacy.
- There are four main types of invasion of privacy:
- Intrusion upon seclusion: Unauthorized entry into someone’s private space or interference with their personal affairs.
- False light: Publication of private information that portrays someone in a false or misleading light.
- Public disclosure of private facts: Publication of private information that is highly offensive and not a matter of public concern.
- Appropriation of name or likeness: Unauthorized use of someone’s name or image for commercial purposes.
- Examples of scenarios where this coverage would be activated include:
- A photographer secretly takes pictures of a celebrity in their home, leading to an intrusion upon seclusion lawsuit.
- A newspaper publishes an article about a private citizen that contains false information, resulting in a false light lawsuit.
Coverage for Copyright Infringement
Copyright infringement occurs when someone uses copyrighted material without permission. This coverage component protects against financial losses arising from lawsuits alleging copyright infringement.
- Copyright law protects original works of authorship, including literary, dramatic, musical, and certain other intellectual works.
- Examples of scenarios where this coverage would be activated include:
- A magazine publishes a photograph without obtaining permission from the copyright holder, leading to a copyright infringement lawsuit.
- A website uses a song without a license, resulting in a copyright infringement lawsuit.
Coverage for Advertising Injury
Advertising injury refers to harm caused by an advertisement or other marketing materials, such as false advertising, disparagement, or infringement of intellectual property rights. This coverage component protects against financial losses arising from lawsuits alleging advertising injury.
- Examples of scenarios where this coverage would be activated include:
- A company publishes an advertisement that makes false claims about its product, leading to an advertising injury lawsuit.
- A radio station broadcasts a commercial that disparages a competitor’s product, resulting in an advertising injury lawsuit.
Coverage for Crisis Management
Crisis management coverage helps media organizations manage and mitigate the financial and reputational risks associated with a crisis, such as a product recall, data breach, or negative media coverage.
- This coverage typically includes:
- Public relations and crisis communications services
- Legal counsel and representation
- Financial assistance for crisis-related expenses
- Examples of scenarios where this coverage would be activated include:
- A television network faces a major scandal involving one of its employees.
- A newspaper publishes an article that triggers a public outcry.
Importance for Media Professionals
In today’s media landscape, where the line between news and opinion is increasingly blurred, and the potential for legal disputes is high, media liability insurance has become an essential tool for safeguarding the financial well-being of media professionals.
This type of insurance acts as a safety net, protecting media professionals from the financial consequences of various risks associated with their work. It can provide peace of mind, allowing them to focus on their craft without the constant worry of potential lawsuits or claims.
Financial Implications of Having and Not Having Media Liability Insurance
The financial implications of having and not having media liability insurance are significant. Consider the following scenarios:
-
Scenario 1: Media Professional with Insurance
Imagine a journalist publishes an article containing factual errors that lead to a defamation lawsuit. The media liability insurance policy covers the legal fees and any potential settlements or judgments against the journalist. This protects the journalist’s personal assets and allows them to continue their work without facing financial ruin. -
Scenario 2: Media Professional Without Insurance
In a similar situation, a journalist without insurance faces the full brunt of the legal costs, settlements, and potential judgments. This could lead to significant financial hardship, potentially forcing them to sell assets or even declare bankruptcy.
The difference between these two scenarios highlights the crucial role of media liability insurance in protecting media professionals from financial ruin.
Types of Media Professionals Who Benefit from This Insurance
A wide range of media professionals can benefit from media liability insurance, including:
- Journalists: Journalists often face accusations of libel, slander, or invasion of privacy. This insurance can cover legal costs and settlements arising from such claims.
- Bloggers and Content Creators: Online content creators, including bloggers, podcasters, and YouTubers, can also be held liable for their content. This insurance can protect them from claims related to defamation, copyright infringement, and other legal issues.
- Photographers and Videographers: Photographers and videographers can face lawsuits for copyright infringement, invasion of privacy, or defamation if their images or videos are used without permission or in a way that causes harm.
- Public Relations Professionals: Public relations professionals often deal with sensitive information and may be involved in situations that could lead to legal claims. This insurance can protect them from liability arising from their work.
Common Claims and Scenarios
Media liability insurance policies are designed to protect media professionals against a wide range of potential claims. These claims can arise from various situations, and understanding common scenarios is crucial for media professionals to mitigate risks and protect their businesses.
Common Claims
Common claims filed under media liability insurance policies often stem from allegations of:
- Libel and Slander: This involves publishing false and defamatory statements that damage someone’s reputation. These claims can arise from inaccurate reporting, biased opinions, or even unintentional errors.
- Invasion of Privacy: Media professionals may face claims for invading someone’s privacy through unauthorized use of images, recording conversations without consent, or disclosing personal information without permission.
- Copyright Infringement: Using copyrighted material without permission, such as photographs, music, or video footage, can lead to copyright infringement claims.
- Negligence: Media professionals can be held liable for negligence if their actions cause harm to others. This could include failing to verify information, publishing inaccurate reports, or creating content that incites violence.
Scenarios Illustrating Common Claims, Media liability insurance
Here are some scenarios that illustrate the common claims mentioned above:
- Libel and Slander: A news website publishes an article accusing a local politician of corruption based on anonymous sources. The politician sues for libel, claiming the accusations are false and damaging to their reputation.
- Invasion of Privacy: A paparazzi photographer captures images of a celebrity in a private setting without their consent. The celebrity sues for invasion of privacy, arguing that their right to privacy was violated.
- Copyright Infringement: A blog uses a copyrighted photograph without permission from the photographer. The photographer sues for copyright infringement, seeking compensation for unauthorized use of their work.
- Negligence: A news report falsely identifies a suspect in a crime, leading to harassment and reputational damage for the wrongly accused individual. The individual sues for negligence, claiming the news organization failed to verify information before publishing.
Mitigating Risks
Media professionals can mitigate these risks through best practices such as:
- Thorough Fact-Checking: Always verify information from multiple sources and use reliable sources. This helps minimize the risk of publishing false or inaccurate information.
- Respecting Privacy: Obtain informed consent before publishing images, recording conversations, or disclosing personal information.
- Understanding Copyright Laws: Be aware of copyright laws and obtain permission before using copyrighted material.
- Maintaining Professional Standards: Adhere to ethical guidelines and professional standards in all aspects of media production and distribution.
- Seeking Legal Counsel: Consult with legal counsel when dealing with sensitive or potentially litigious situations.
Exclusions and Limitations
Like any insurance policy, media liability insurance comes with certain exclusions and limitations. Understanding these aspects is crucial to ensure you have adequate coverage for your specific needs. These exclusions are not designed to be punitive but rather to define the scope of the policy and manage risk effectively.
Common Exclusions
Exclusions are specific events or situations that are not covered by the insurance policy. Understanding these exclusions is essential to avoid surprises and ensure you have appropriate coverage.
- Intentional Acts: Most policies exclude coverage for claims arising from intentional acts of libel, slander, or copyright infringement. This means if you knowingly publish false information with the intent to harm someone’s reputation, you won’t be covered.
- Personal Injury: Media liability insurance typically does not cover claims related to personal injury, such as physical harm or emotional distress, unless directly linked to a covered media-related incident.
- Prior Acts: Policies usually exclude coverage for claims arising from events that occurred before the policy’s effective date. This is a common practice across most insurance types.
- Criminal Acts: Coverage for claims arising from criminal acts, such as theft or fraud, is generally excluded. This is due to the inherently different nature of criminal acts compared to media-related liability.
- Employee Misconduct: Policies may exclude coverage for claims arising from employee misconduct that is not directly related to their professional media duties. For example, if an employee commits a crime unrelated to their work, it might not be covered.
- Certain Types of Publications: Some policies exclude coverage for specific types of publications, such as hate speech, pornography, or material that incites violence. This reflects the insurer’s risk assessment and ethical considerations.
Common Limitations
Limitations are restrictions on the amount or scope of coverage provided by the policy. Understanding these limitations is important to ensure you have adequate coverage for your specific needs.
- Policy Limits: Each media liability policy has a maximum amount of coverage, known as the policy limit. This limit represents the maximum amount the insurer will pay for covered claims during a policy period.
- Deductibles: Many policies require you to pay a deductible, which is a fixed amount you are responsible for paying before the insurer covers the rest of the claim. Deductibles can help keep premiums lower, but you should factor them into your budget.
- Coverage Period: Media liability insurance typically covers claims arising during the policy period. This means that if a claim is filed after the policy expires, it may not be covered.
- Claims Reporting Requirements: Most policies have specific requirements for reporting claims. Failure to meet these requirements could affect your coverage.
Impact of Exclusions and Limitations
Exclusions and limitations can significantly impact your coverage and leave you financially exposed if you face a media-related claim. It’s essential to carefully review your policy and understand these provisions to ensure you have adequate protection.
- Financial Risk: Exclusions and limitations can expose you to significant financial risk if you face a claim that is not covered. For example, if you are sued for libel and your policy excludes intentional acts, you could be responsible for all legal costs and damages.
- Limited Protection: Exclusions and limitations can reduce the scope of your coverage, leaving you with less protection than you might expect. For example, if your policy has a low policy limit, you may not receive enough compensation to cover all your losses if you face a significant claim.
- Increased Liability: Exclusions and limitations can increase your personal liability if you face a claim that is not covered. This means you could be personally responsible for paying any damages awarded to the claimant.
Table of Common Exclusions and Implications
| Exclusion | Implications |
|---|---|
| Intentional Acts | No coverage for claims arising from knowingly publishing false information with the intent to harm someone’s reputation. |
| Personal Injury | No coverage for claims related to physical harm or emotional distress unless directly linked to a covered media-related incident. |
| Prior Acts | No coverage for claims arising from events that occurred before the policy’s effective date. |
| Criminal Acts | No coverage for claims arising from criminal acts, such as theft or fraud. |
| Employee Misconduct | No coverage for claims arising from employee misconduct that is not directly related to their professional media duties. |
| Certain Types of Publications | No coverage for specific types of publications, such as hate speech, pornography, or material that incites violence. |
Choosing the Right Policy
Navigating the world of media liability insurance can feel overwhelming, but finding the right policy is crucial for protecting your career and financial well-being. A well-tailored policy provides peace of mind, knowing you’re covered in the event of unforeseen legal issues.
Factors to Consider
Selecting the right media liability insurance policy requires careful consideration of several key factors. This ensures that your coverage aligns with your specific needs and potential risks.
- Type of Media Work: The type of media work you do significantly impacts the risks you face. For example, a journalist working on investigative reporting may need broader coverage than a freelance photographer specializing in portraits.
- Coverage Limits: Coverage limits determine the maximum amount your insurance provider will pay for a claim. It’s important to choose limits that reflect the potential financial impact of a lawsuit.
- Deductible: The deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance kicks in. A higher deductible typically means lower premiums, but you’ll need to be prepared to cover more upfront in case of a claim.
- Policy Exclusions: All policies have exclusions, which are specific situations or types of claims that are not covered. It’s crucial to understand these exclusions to avoid surprises later.
- Reputation of the Insurer: Research the financial stability and reputation of potential insurers. Look for companies with a strong track record of handling claims fairly and efficiently.
Essential Questions for Insurance Providers
Asking the right questions is essential to ensure you fully understand the policy’s terms and coverage.
- What specific types of media work are covered by the policy? This clarifies the scope of your protection.
- What are the policy’s coverage limits and deductibles? Understanding these figures helps you determine the financial protection offered.
- What are the key exclusions and limitations of the policy? This helps you avoid potential gaps in coverage.
- What is the claims process like? Knowing the process for filing and handling claims ensures a smooth experience in case of an incident.
- Does the policy offer legal defense coverage? This ensures you have legal representation in case of a lawsuit.
- Are there any discounts available for bundling policies or for specific types of media work? This can help you save money on your insurance premiums.
Negotiating Favorable Terms
Once you’ve identified a few potential insurers, it’s time to negotiate favorable terms and coverage levels.
- Compare Quotes: Get quotes from multiple insurers to compare premiums and coverage options. This helps you find the best value for your needs.
- Ask for Discounts: Inquire about discounts for bundling policies, professional memberships, or safety training courses.
- Review the Policy Carefully: Before signing any policy, carefully review the terms and conditions to ensure you understand the coverage and exclusions.
- Don’t Be Afraid to Negotiate: Insurance providers are often willing to negotiate terms, especially if you have a strong track record and a good understanding of your needs.
Risk Management Strategies
Proactive risk management is crucial for media professionals to mitigate potential liabilities and protect their businesses. By implementing effective strategies, media professionals can minimize the likelihood of claims, reduce financial burdens, and safeguard their reputation.
Strategies to Minimize Media-Related Risks
Implementing effective risk management strategies can significantly reduce the likelihood of claims and protect media professionals from potential liabilities. Here are some key strategies:
Understanding Media Law and Regulations
It is essential for media professionals to stay informed about relevant media laws, regulations, and ethical guidelines. This includes understanding laws related to defamation, privacy, copyright, and intellectual property. By adhering to these laws and regulations, media professionals can minimize the risk of legal action.
Developing Clear Policies and Procedures
Establishing clear policies and procedures for content creation, review, and distribution can help prevent errors and ensure compliance with legal requirements. These policies should cover aspects such as:
- Content verification and fact-checking
- Obtaining necessary permissions and releases
- Copyright and intellectual property usage
- Handling confidential information
- Social media and online communication
Implementing Robust Fact-Checking Processes
Thorough fact-checking is essential to prevent errors and misinformation that could lead to legal claims. This involves verifying information from multiple sources, cross-referencing data, and seeking expert opinions when necessary.
Utilizing Legal Counsel
Engaging legal counsel specializing in media law can provide valuable guidance on legal compliance, risk assessment, and potential legal issues. Consulting with legal counsel can help media professionals identify potential risks, develop effective risk management strategies, and address specific legal challenges.
Maintaining Accurate Records
Keeping accurate records of all media-related activities, including content creation, publication, and distribution, is crucial for legal defense. These records can provide evidence of compliance, fact-checking, and proper procedures in case of legal disputes.
Providing Adequate Training
Providing training to staff on media law, ethical guidelines, and best practices can help minimize risks. This training should cover topics such as:
- Defamation and libel
- Privacy laws and regulations
- Copyright and intellectual property
- Social media best practices
- Crisis communication
Utilizing Risk Assessment Tools
Several risk assessment tools and software programs are available to help media professionals identify and assess potential risks. These tools can provide valuable insights into areas of vulnerability and guide the development of effective risk mitigation strategies.
Implementing Insurance Coverage
Media liability insurance is a crucial aspect of risk management. This insurance policy provides financial protection against claims arising from media-related activities. It can cover legal expenses, settlements, and judgments, protecting media professionals from significant financial losses.
Best Practices for Managing Media-Related Risks
Following best practices can help media professionals mitigate risks and minimize the likelihood of claims. Here are some essential best practices:
- Obtain written consent: Always obtain written consent from individuals before using their name, image, or likeness in any media content. This is crucial for protecting against privacy claims.
- Verify information: Thoroughly verify all information before publishing or broadcasting. Use multiple sources, cross-reference data, and consult with experts when necessary.
- Attribute sources: Clearly attribute all sources of information to avoid plagiarism and copyright infringement claims.
- Be aware of copyright laws: Understand copyright laws and obtain necessary permissions before using copyrighted material.
- Use disclaimers: Use clear disclaimers to indicate opinions, assumptions, or limitations of liability.
- Monitor social media: Actively monitor social media platforms for potential risks and address any issues promptly.
- Train staff: Provide regular training to staff on media law, ethical guidelines, and best practices.
- Maintain accurate records: Keep detailed records of all media-related activities, including content creation, publication, and distribution.
- Consult legal counsel: Regularly consult with legal counsel specializing in media law to stay informed about legal developments and address potential risks.
Future Trends in Media Liability Insurance
The media landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer habits. These shifts are having a significant impact on media liability insurance, leading to new coverage needs and evolving risk profiles. Understanding these trends is crucial for media professionals and insurance providers alike, as they navigate the evolving media landscape.
Increased Coverage for Emerging Technologies
The rapid adoption of new technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), virtual reality (VR), and augmented reality (AR) is creating new risks and coverage needs for media professionals. For instance, AI-powered content creation tools raise concerns about copyright infringement and potential biases embedded in algorithms. VR and AR experiences introduce unique liability risks related to user safety and potential psychological harm. Media liability insurance policies will need to adapt to these emerging technologies, offering coverage for new risks and liabilities.
Cybersecurity and Data Privacy Concerns
Data breaches and cyberattacks are becoming increasingly common, posing significant risks to media organizations. Media liability insurance policies are evolving to address these concerns, providing coverage for cyber extortion, data breach response costs, and regulatory fines related to data privacy violations. This trend is likely to continue as media organizations increasingly rely on digital platforms and collect vast amounts of personal data.
Social Media Liability
Social media platforms have become integral to media operations, offering new avenues for communication and content distribution. However, they also present unique liability risks, including defamation, invasion of privacy, and copyright infringement. Media liability insurance policies are expanding to address these risks, offering coverage for social media-related claims and providing guidance on managing social media risk.
Increased Focus on Crisis Management
In today’s fast-paced media environment, crises can erupt quickly and have a significant impact on a media organization’s reputation and financial stability. Media liability insurance policies are increasingly incorporating crisis management services, providing support for responding to crises, managing public relations, and mitigating potential damage. This trend reflects the growing importance of proactive crisis management in today’s media landscape.
Final Wrap-Up
Media liability insurance is a cornerstone of responsible media practice, empowering professionals to navigate the complex landscape of their profession with confidence. By understanding the intricacies of this coverage, media professionals can make informed decisions, manage risks effectively, and safeguard their future. Whether you are a seasoned veteran or just starting your journey in the media world, investing in media liability insurance is a prudent step towards ensuring a secure and fulfilling career.
Media liability insurance is a crucial protection for businesses operating in today’s digital world. It covers a range of potential risks, including defamation, copyright infringement, and privacy violations. While Colonial Penn Life Insurance Company colonial penn life insurance company focuses on life insurance, media liability insurance is a separate but equally important consideration for organizations that create and distribute content.