How much is health insurance per month? This question is on the minds of many individuals seeking coverage. Understanding the factors that influence health insurance costs is crucial for making informed decisions about your health and finances. From age and health status to location and plan type, a multitude of variables contribute to the monthly premium you pay.
Navigating the world of health insurance can be overwhelming, especially when faced with different plans, deductibles, and co-pays. This guide aims to demystify the process by providing comprehensive information on average premiums, key considerations, and strategies for finding affordable coverage that meets your needs.
Factors Influencing Health Insurance Costs
The price of health insurance can vary greatly depending on a number of factors. Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions about your health insurance coverage.
Age
Age is one of the most significant factors influencing health insurance premiums. Generally, younger individuals tend to have lower premiums compared to older individuals. This is because younger people are statistically less likely to require extensive medical care. As individuals age, the likelihood of health issues and healthcare utilization increases, leading to higher premiums. For example, a 25-year-old might pay a significantly lower monthly premium than a 65-year-old, even with similar health status and coverage.
Health Status
Your health status also plays a crucial role in determining your health insurance premium. Individuals with pre-existing conditions or a history of significant medical expenses often face higher premiums. This is because insurance companies assess the risk of covering individuals based on their health history. For instance, someone with diabetes or a history of heart disease might pay a higher premium compared to someone with no pre-existing conditions.
Location
The location where you reside can also influence your health insurance costs. Factors like the cost of living, healthcare provider density, and prevalence of certain diseases in a particular area can impact premiums. For example, premiums in metropolitan areas with high healthcare costs might be higher than in rural areas with lower healthcare costs.
Coverage Type
The type of health insurance coverage you choose significantly affects your monthly premium. Individual health insurance plans, which cover only you, typically have lower premiums compared to family plans that cover multiple individuals. Employer-sponsored health insurance plans, offered through your employer, can vary in cost depending on the employer’s contribution and the plan’s features.
Health Insurance Plan
Health insurance plans are categorized into different tiers based on their coverage levels and premiums. Bronze plans offer the lowest premiums but have the highest out-of-pocket costs. Platinum plans offer the highest coverage but come with the highest premiums. Silver and gold plans fall in between, offering a balance of coverage and cost. For instance, a bronze plan might have a lower monthly premium but require you to pay a larger portion of your healthcare expenses out-of-pocket, while a platinum plan might have a higher monthly premium but cover a greater share of your healthcare costs.
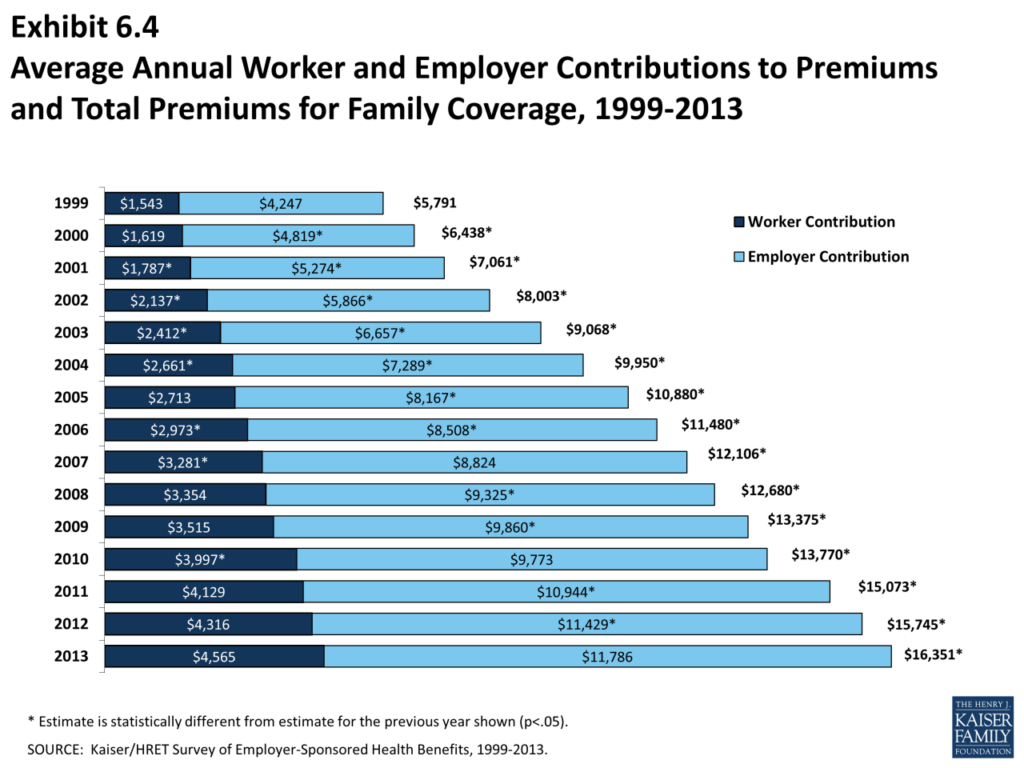
Average Health Insurance Premiums
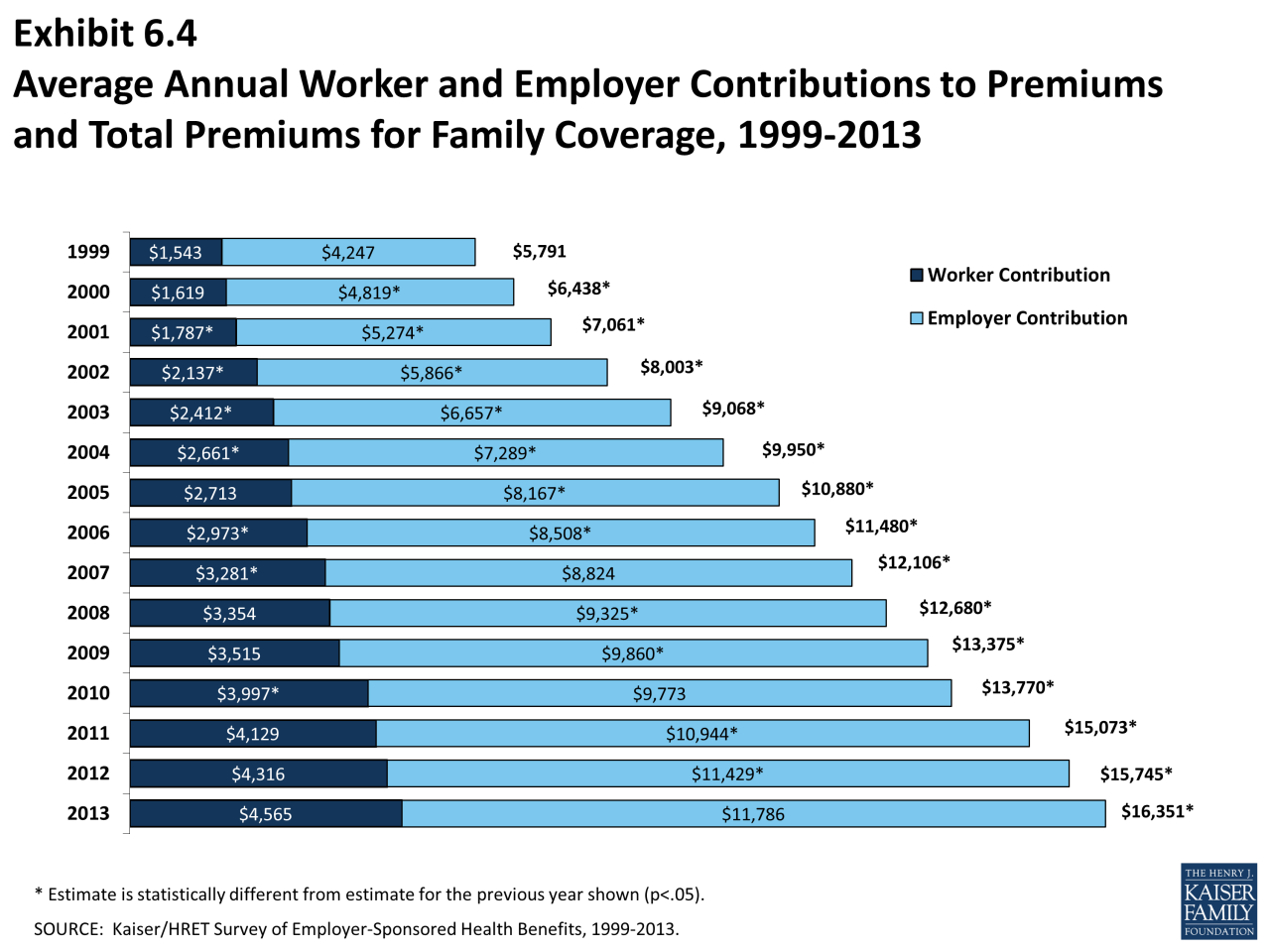
The cost of health insurance varies significantly depending on factors like age, location, coverage level, and health status. To understand the average costs, let’s explore the different types of health insurance plans and their associated premiums.
Average Monthly Premiums for Individual Health Insurance Plans
Individual health insurance plans are purchased by individuals, not through an employer. The average monthly cost of individual health insurance plans varies widely across different states.
- California: $500 – $700
- Texas: $400 – $600
- Florida: $450 – $650
- New York: $600 – $800
- Illinois: $550 – $750
Average Monthly Premiums for Family Health Insurance Plans
Family health insurance plans cover multiple individuals, typically spouses and dependents. Here’s a table showcasing the average monthly premiums for family health insurance plans, categorized by state:
| State | Average Monthly Premium |
|---|---|
| California | $1,200 – $1,800 |
| Texas | $1,000 – $1,500 |
| Florida | $1,100 – $1,600 |
| New York | $1,500 – $2,200 |
| Illinois | $1,300 – $1,900 |
Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance Plans
Employer-sponsored health insurance plans are offered by employers to their employees. The typical monthly cost of employer-sponsored health insurance plans varies depending on the employer’s contribution and the employee’s chosen plan.
On average, employees contribute around 18% of the total premium cost, while employers contribute the remaining 82%.
Understanding Health Insurance Costs
Understanding the components of health insurance costs is crucial for making informed decisions about your coverage. Several factors influence the price of your monthly premiums, and it’s essential to grasp how they impact your overall expenses.
Components of Health Insurance Premiums
Health insurance premiums are the monthly payments you make to your insurance company in exchange for coverage. These premiums are determined by various factors, including:
- Age: Younger individuals generally have lower health insurance premiums than older individuals, as they tend to be healthier and require less medical care.
- Location: Premiums can vary based on your geographic location. Areas with higher healthcare costs or a greater concentration of older adults may have higher premiums.
- Health Status: People with pre-existing health conditions often face higher premiums, as they are more likely to require medical care. However, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) prohibits insurance companies from denying coverage or charging higher premiums based solely on pre-existing conditions.
- Tobacco Use: Smokers typically pay higher premiums due to the increased risk of health problems associated with smoking.
- Plan Type: Different health insurance plans offer varying levels of coverage and benefits, impacting their premium costs. For example, a comprehensive plan with low deductibles and co-pays will generally be more expensive than a high-deductible plan with limited coverage.
- Employer Contributions: If you receive health insurance through your employer, your employer may contribute a portion of the premium cost. The amount your employer contributes can affect your out-of-pocket expenses.
Deductibles and Co-pays
Deductibles and co-pays are out-of-pocket expenses you incur before your health insurance coverage kicks in.
- Deductible: This is the amount you must pay out-of-pocket for healthcare services before your insurance starts covering the costs. Once you meet your deductible, your insurance will typically cover the remaining costs, subject to co-pays and coinsurance.
- Co-pay: This is a fixed amount you pay for specific medical services, such as doctor’s visits or prescriptions. Co-pays are typically lower than deductibles and apply after you’ve met your deductible.
Deductibles and co-pays can significantly impact your monthly expenses, particularly if you have a high deductible plan or require frequent medical care.
Out-of-Pocket Maximums
An out-of-pocket maximum is the maximum amount you’ll pay for healthcare expenses in a given year. Once you reach this limit, your insurance will cover 100% of your eligible medical costs for the rest of the year.
Out-of-pocket maximums can help protect you from high medical bills and provide a sense of financial security. However, it’s essential to understand that this limit applies only to covered medical expenses and does not include premiums, deductibles, or co-pays.
Factors Influencing Plan Costs
The table below Artikels key factors that can influence the cost of specific health insurance plans:
| Factor | Impact on Plan Cost |
|---|---|
| Plan Type (e.g., HMO, PPO, EPO) | Different plan types offer varying levels of coverage and network restrictions, impacting premium costs. |
| Network Size | Plans with broader networks (more healthcare providers) tend to have higher premiums but offer greater flexibility in choosing doctors and hospitals. |
| Prescription Drug Coverage | Plans with comprehensive prescription drug coverage may have higher premiums but can save you money on medications. |
| Benefits and Services | Plans with additional benefits, such as dental or vision coverage, may have higher premiums. |
Affordable Health Insurance Options: How Much Is Health Insurance Per Month
Finding affordable health insurance can be a challenge, but it’s possible with the right resources and strategies. Several options are available to help you navigate the costs of health insurance and find a plan that fits your budget.
Government Programs and Subsidies
Government programs and subsidies can significantly reduce the cost of health insurance. These programs are designed to help individuals and families with lower incomes afford health coverage.
- Marketplace Subsidies: The Affordable Care Act (ACA) provides financial assistance, known as subsidies, to eligible individuals and families who purchase health insurance through the Health Insurance Marketplace. These subsidies are based on income and family size, and they can significantly reduce monthly premiums.
- Medicaid: Medicaid is a government-funded health insurance program for low-income individuals and families. Eligibility for Medicaid varies by state, but it typically covers essential health services, including doctor visits, hospitalizations, and prescription drugs.
- CHIP (Children’s Health Insurance Program): CHIP provides health insurance coverage to children in families with incomes too high to qualify for Medicaid but too low to afford private health insurance.
Strategies for Finding Affordable Health Insurance
Several strategies can help you find affordable health insurance plans that meet your needs.
- Compare Plans: Use online tools or contact an insurance broker to compare plans from different insurance companies. Consider factors like premiums, deductibles, copayments, and coverage levels.
- Consider High-Deductible Plans: High-deductible health plans (HDHPs) typically have lower monthly premiums but higher deductibles. They can be a good option for healthy individuals who don’t anticipate frequent medical expenses.
- Explore HSA (Health Savings Account): HDHPs often qualify for a Health Savings Account (HSA). An HSA allows you to save pre-tax dollars for medical expenses. The money in an HSA rolls over year to year, and it can be used for future medical costs.
- Negotiate with Your Employer: If you have employer-sponsored health insurance, discuss your options with your human resources department. You may be able to negotiate a lower premium or choose a different plan.
Comparing Health Insurance Plans
Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of different health insurance plans is essential for making an informed decision.
| Plan Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Health Insurance |
|
|
| High-Deductible Health Plan (HDHP) |
|
|
| Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) |
|
|
| Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) |
|
|
Health Insurance Coverage and Benefits
Health insurance plans are designed to provide financial protection against the high costs of medical care. They offer a range of coverage and benefits, varying depending on the plan type and insurer. Understanding these benefits is crucial to choosing the right plan for your needs and budget.
Essential Benefits
Most health insurance plans in the United States are required to cover essential health benefits mandated by the Affordable Care Act (ACA). These benefits include:
- Ambulatory patient services: Outpatient care, such as doctor visits, lab tests, and preventive screenings.
- Emergency services: Treatment for unexpected medical conditions.
- Hospitalization: Inpatient care for illnesses or injuries.
- Maternity and newborn care: Pregnancy, childbirth, and postpartum care.
- Mental health and substance use disorder services: Treatment for mental health conditions and substance abuse.
- Prescription drugs: Coverage for medications prescribed by a doctor.
- Rehabilitative services and devices: Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and durable medical equipment.
- Preventive and wellness services: Screenings, vaccinations, and health education programs.
Coverage Differences Between Plan Types
Different types of health insurance plans offer varying levels of coverage and benefits. Here’s a comparison of some common plan types:
| Plan Type | Coverage | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) | Limited network of providers. | Lower premiums, preventive care, limited out-of-network coverage. |
| Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) | Wider network of providers. | Higher premiums, greater flexibility, out-of-network coverage with higher costs. |
| Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO) | Similar to HMO, but with slightly wider network. | Lower premiums than PPO, limited out-of-network coverage. |
| Point-of-Service (POS) | Combines features of HMO and PPO. | Moderate premiums, some out-of-network coverage. |
Specific Benefits Offered by Various Plans
Preventive Care
Many plans offer preventive care services at no cost to the insured. This includes screenings for conditions like cancer, diabetes, and heart disease, as well as vaccinations and health counseling.
Prescription Drugs
Prescription drug coverage varies significantly between plans. Some plans have formularies, which are lists of approved medications. Others may have tiered copayments, where the cost of a drug depends on its tier.
Mental Health Services
The ACA requires most health insurance plans to cover mental health and substance use disorder services. This includes therapy, medication, and inpatient treatment.
Health Insurance Market Trends
The health insurance market is constantly evolving, driven by factors such as technological advancements, changing demographics, and evolving healthcare policies. Understanding these trends is crucial for individuals and businesses alike, as it can help inform decisions about coverage and costs.
Impact of Healthcare Reforms and Legislation, How much is health insurance per month
Healthcare reforms and legislation have significantly impacted the health insurance market. The Affordable Care Act (ACA), enacted in 2010, has had a profound influence on health insurance costs and coverage. The ACA introduced several key provisions, including the individual mandate, which required most Americans to have health insurance or face a penalty. The ACA also expanded Medicaid eligibility, providing health insurance coverage to millions of low-income Americans.
The ACA’s impact on health insurance costs has been mixed. While the law has helped to slow the growth of premiums, it has also led to higher out-of-pocket costs for some consumers.
The ACA has also spurred innovation in the health insurance market, with the emergence of new types of plans, such as health insurance exchanges and marketplace plans. These exchanges provide a platform for individuals to compare and purchase health insurance plans from different insurers.
Future Outlook for Health Insurance Premiums and Plan Options
The future outlook for health insurance premiums and plan options is uncertain. Several factors will likely influence the market in the coming years, including:
- The ongoing impact of the ACA, including potential changes to the law.
- The rising costs of healthcare, driven by factors such as technological advancements and an aging population.
- The growth of consumer-driven health plans, which give individuals more control over their healthcare spending.
- The increasing adoption of telemedicine and other virtual healthcare services.
Experts predict that health insurance premiums will continue to rise in the coming years, but at a slower pace than in the past. The growth of consumer-driven health plans and the adoption of virtual healthcare services are expected to help contain costs.
The health insurance market is likely to continue to evolve in response to these trends, with new plan options and coverage models emerging. Individuals and businesses will need to stay informed about these changes to make informed decisions about their health insurance needs.
Health Insurance Resources and Information
Navigating the world of health insurance can be overwhelming, especially with the wide array of plans and coverage options available. Fortunately, numerous resources and organizations exist to guide individuals through this process. This section explores valuable resources that provide information and support to help you make informed decisions about your health insurance.
Government Agencies
Government agencies play a crucial role in providing information and assistance related to health insurance. They offer guidance on eligibility for government-sponsored programs, enrollment procedures, and plan options.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS): The CMS is the federal agency responsible for administering Medicare, Medicaid, and the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP). It provides comprehensive information about these programs, including eligibility criteria, benefits, and enrollment procedures. Visit their website at https://www.cms.gov/ or call 1-800-MEDICARE (1-800-633-4227).
- State Health Insurance Assistance Program (SHIP): SHIP is a free and confidential program available in every state that provides counseling and assistance to individuals seeking health insurance. SHIP counselors can help you understand your options, compare plans, and navigate the enrollment process. To find your state’s SHIP program, visit https://www.shiptacenter.org/ or contact your state’s Department of Insurance.
Non-Governmental Organizations
Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) provide valuable resources and support to individuals seeking information about health insurance. These organizations often focus on specific populations, such as low-income individuals, seniors, or those with pre-existing conditions.
- Health Insurance Marketplace (Healthcare.gov): The Health Insurance Marketplace is a website operated by the federal government where individuals can compare and enroll in health insurance plans offered through the Affordable Care Act (ACA). You can access the Marketplace at https://www.healthcare.gov/ or call 1-800-318-2596.
- Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF): The KFF is a non-profit organization that provides in-depth research and analysis on health care policy, including health insurance. Their website offers comprehensive information about health insurance trends, coverage options, and affordability. Visit their website at https://www.kff.org/.
- National Patient Advocate Foundation (NPAF): The NPAF is a non-profit organization that advocates for patients’ rights and provides resources on health insurance and healthcare access. Their website offers information about patient rights, appeals processes, and resources for navigating the healthcare system. Visit their website at https://www.npaf.org/.
Online Resources
The internet offers a wealth of information about health insurance. Numerous websites and tools can help you compare plans, estimate costs, and understand your coverage options.
- eHealthInsurance: eHealthInsurance is a leading online marketplace for health insurance plans. Their website allows you to compare plans from different insurers, get quotes, and enroll online. Visit their website at https://www.ehealthinsurance.com/.
- HealthPocket: HealthPocket is a website that provides comprehensive information about health insurance plans and coverage. Their website offers tools to compare plans, estimate costs, and understand your benefits. Visit their website at https://www.healthpocket.com/.
- Healthfinder.gov: Healthfinder.gov is a website operated by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services that provides information about health insurance and other health-related topics. Their website offers resources on finding affordable health insurance, understanding your coverage, and accessing health care services. Visit their website at https://www.healthfinder.gov/.
Table of Resources
| Resource | Description | Website | Phone Number |
|—|—|—|—|
| Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) | Federal agency responsible for Medicare, Medicaid, and CHIP | https://www.cms.gov/ | 1-800-MEDICARE (1-800-633-4227) |
| State Health Insurance Assistance Program (SHIP) | Free and confidential program providing counseling and assistance with health insurance | https://www.shiptacenter.org/ | Contact your state’s Department of Insurance |
| Health Insurance Marketplace (Healthcare.gov) | Website for comparing and enrolling in ACA health insurance plans | https://www.healthcare.gov/ | 1-800-318-2596 |
| Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF) | Non-profit organization providing research and analysis on health care policy | https://www.kff.org/ | N/A |
| National Patient Advocate Foundation (NPAF) | Non-profit organization advocating for patients’ rights and providing resources on health insurance | https://www.npaf.org/ | N/A |
| eHealthInsurance | Online marketplace for comparing and enrolling in health insurance plans | https://www.ehealthinsurance.com/ | N/A |
| HealthPocket | Website providing information and tools for comparing health insurance plans | https://www.healthpocket.com/ | N/A |
| Healthfinder.gov | Website providing information about health insurance and other health-related topics | https://www.healthfinder.gov/ | N/A |
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding how much health insurance costs per month requires a thorough evaluation of individual factors, plan options, and available resources. By carefully considering your health needs, budget, and coverage requirements, you can make an informed decision that provides peace of mind and financial stability. Remember, health insurance is a vital investment in your well-being, and taking the time to research and choose the right plan can pay dividends in the long run.
The cost of health insurance varies widely depending on factors like age, location, and coverage. It’s important to shop around and compare plans to find the best value for your needs. While you’re looking for insurance, you might also want to consider errors & omissions insurance , which can protect professionals from liability claims.
Ultimately, the cost of health insurance is a significant factor for many individuals and families, and it’s crucial to make informed decisions about coverage.