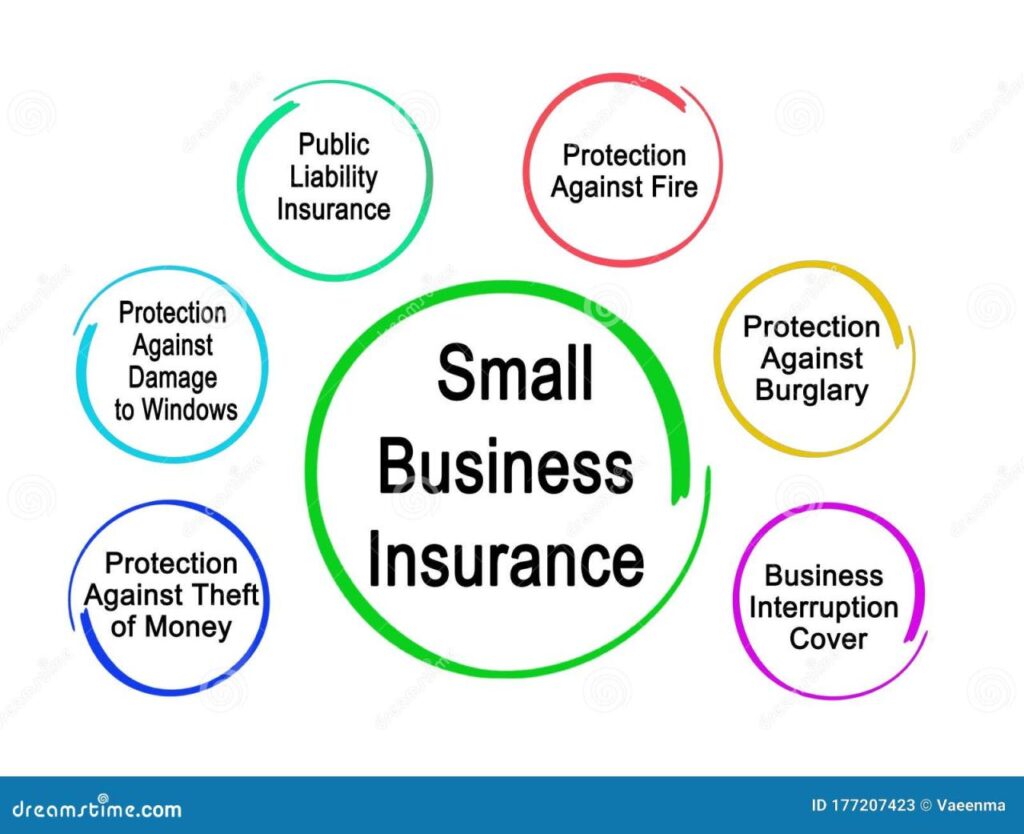
Insurance for small businesses is crucial for safeguarding your financial well-being and ensuring your company’s survival. While starting a business is exciting, it also comes with inherent risks that can significantly impact your operations. From property damage to lawsuits, unexpected events can arise, leading to substantial financial losses. This guide provides an overview of essential insurance types for small businesses, highlighting the importance of coverage and how to navigate the insurance landscape.
Understanding your specific needs is key. The right insurance policies can provide a safety net, protecting your assets, employees, and customers. We’ll explore various insurance options, including general liability, property insurance, workers’ compensation, and additional coverage like business interruption and cyber liability. We’ll also delve into choosing the right insurance provider, understanding policy terms, and implementing risk management strategies to mitigate potential losses.
Understanding Small Business Insurance Needs: Insurance For Small Businesses
Small businesses, while vital to the economy, face unique risks that differ from large corporations. These risks can be significant and potentially devastating to their operations and financial stability. Therefore, understanding the specific insurance needs of small businesses is crucial for their long-term success.
Types of Insurance for Small Businesses
Understanding the specific types of insurance needed for a small business is critical for mitigating risks and ensuring financial security.
- Property Insurance: This type of insurance covers losses to your business property, including buildings, equipment, inventory, and other assets, due to events like fire, theft, vandalism, or natural disasters. For example, if a fire damages your storefront, property insurance would cover the cost of repairs or replacement.
- Liability Insurance: This coverage protects your business from financial losses arising from claims of negligence, injury, or property damage caused by your business or employees. This is essential in situations where a customer is injured on your premises or a product your business manufactures causes harm.
- Workers’ Compensation Insurance: This insurance is mandatory in most states and provides coverage for employees injured on the job. It covers medical expenses, lost wages, and other benefits related to work-related injuries or illnesses. For instance, if an employee falls and breaks their leg while working, workers’ compensation would cover their medical bills and lost wages during their recovery.
- Business Interruption Insurance: This coverage protects your business from financial losses incurred due to a temporary shutdown caused by an insured event. It can help cover expenses like rent, utilities, and payroll while your business is unable to operate. For example, if a major storm forces your business to close for several weeks, business interruption insurance would help cover the lost income during that time.
Additional Insurance Considerations for Small Businesses
Beyond the core insurance policies, several additional insurance considerations can significantly benefit small businesses. These policies address specific risks that can arise due to unforeseen circumstances, protecting your business from financial hardship and ensuring its continuity.
Business Interruption Insurance, Insurance for small businesses
Business interruption insurance is a crucial safeguard against lost income resulting from unforeseen events that disrupt your business operations. These events could include natural disasters like fires, floods, or earthquakes, or man-made events like power outages, vandalism, or even government-imposed closures due to pandemics.
- Covers Lost Revenue: This insurance provides financial support to cover lost revenue during the period your business is unable to operate due to a covered event.
- Contingency Planning: It helps businesses plan for potential disruptions by providing funds to cover essential expenses like rent, utilities, salaries, and loan payments.
- Business Continuity: By mitigating financial losses, business interruption insurance enables businesses to recover faster and resume operations, minimizing long-term impact.
Professional Liability Insurance (Errors and Omissions)
Professional liability insurance, also known as errors and omissions (E&O) insurance, is essential for businesses providing professional services, such as consulting, accounting, legal, or design services. It protects against claims arising from professional negligence, mistakes, or omissions in the services provided.
- Protects Against Claims: E&O insurance covers legal defense costs and financial settlements in case a client files a claim alleging negligence or malpractice.
- Maintains Reputation: By providing financial protection, E&O insurance helps businesses maintain their reputation and avoid costly legal battles that can damage their brand image.
- Peace of Mind: It offers peace of mind for professionals by ensuring they are protected from potential financial risks associated with their services.
Cyber Liability Insurance
In the digital age, businesses are increasingly vulnerable to cyberattacks and data breaches. Cyber liability insurance safeguards businesses against financial losses and legal liabilities resulting from such incidents.
- Data Breach Response: Cyber liability insurance covers the costs associated with responding to a data breach, including notification, credit monitoring, and legal expenses.
- Business Interruption: It can provide financial support for lost revenue and expenses if a cyberattack disrupts business operations.
- Reputation Management: Cyber liability insurance helps businesses manage the reputational damage caused by a data breach, including public relations and crisis management services.
Choosing the Right Insurance Provider for Small Businesses
Finding the right insurance provider is crucial for any small business. You need a company that offers comprehensive coverage, competitive pricing, and excellent customer service. This section will help you navigate the insurance landscape and find the best fit for your business.
Comparing Insurance Providers
When comparing insurance providers, it’s essential to consider their strengths and weaknesses across several key areas:
- Coverage: Look for a provider that offers a wide range of coverage options tailored to your specific industry and business needs. For example, if you own a restaurant, you’ll need coverage for food spoilage, slip-and-fall accidents, and other unique risks. Consider the limits and exclusions of each policy to ensure they meet your requirements.
- Pricing: Compare quotes from different providers to find the most competitive rates. Don’t just focus on the lowest price; ensure the coverage offered is sufficient for your needs. Factors like your business size, industry, location, and risk profile can influence pricing.
- Customer Service: Read reviews and testimonials from other businesses to assess the provider’s reputation for customer service. You want a company that is responsive, helpful, and easy to work with, especially when you need to file a claim.
Evaluating Financial Stability and Reputation
It’s crucial to choose a financially stable insurance company that can fulfill its obligations when you need to file a claim. Here are some ways to assess their financial health and reputation:
- Financial Ratings: Look for ratings from reputable agencies like A.M. Best, Standard & Poor’s, and Moody’s. These ratings reflect the company’s financial strength and ability to pay claims.
- Industry Reputation: Check online reviews, industry publications, and forums to see what other businesses say about the provider’s reputation for claims handling and customer satisfaction.
- Financial Stability: Research the company’s financial statements and annual reports to understand its profitability, cash flow, and overall financial health. A company with a strong track record of profitability and financial stability is more likely to be around to pay your claims in the future.
The Role of Insurance Brokers
Insurance brokers act as intermediaries between businesses and insurance companies. They can help you navigate the complex world of insurance and find the best coverage options at the most competitive prices. Here’s how they can benefit your business:
- Expertise: Brokers have extensive knowledge of the insurance market and can identify the most suitable policies for your specific needs.
- Negotiation: They can negotiate better rates and terms with insurance companies on your behalf, leveraging their relationships and experience.
- Comparison: They can compare quotes from multiple providers, saving you time and effort in the process.
- Claims Support: They can provide guidance and support throughout the claims process, ensuring a smooth and efficient experience.
Understanding Insurance Policy Terms and Conditions

Navigating the world of insurance can be overwhelming, especially for small business owners. It’s crucial to understand the terminology used in insurance policies to make informed decisions and ensure you have the right coverage. This section delves into key insurance policy terms, provides tips for negotiating favorable coverage, and Artikels the process for filing and managing insurance claims.
Insurance is essential for small businesses to protect against unexpected risks, and that includes insuring their vehicles. Finding affordable coverage can be a challenge, but there are resources available to help, such as websites offering cheap automotive insurance.
By securing competitive rates on their vehicles, small businesses can free up valuable funds for other operational needs and continue to thrive.
Common Insurance Policy Terms
Understanding common insurance policy terms is essential for grasping the scope of your coverage and the associated costs. Here are some key terms to familiarize yourself with:
- Deductible: This is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance policy kicks in to cover the remaining costs. A higher deductible typically results in lower premiums. For example, if you have a $500 deductible for your property insurance and experience a $10,000 loss, you would pay the first $500 and your insurance would cover the remaining $9,500.
- Premium: The premium is the regular payment you make to your insurance provider for coverage. Premiums are usually calculated based on factors like the type of coverage, your business’s size, risk level, and location.
- Coverage Limits: Coverage limits define the maximum amount your insurance policy will pay for a covered event. For instance, a liability insurance policy may have a coverage limit of $1 million per occurrence, meaning the insurer will pay up to $1 million for a single claim.
Negotiating Insurance Policy Terms
Negotiating insurance policy terms can help you secure the most favorable coverage for your business. Here are some tips for successful negotiation:
- Shop around: Obtain quotes from multiple insurance providers to compare coverage options and premiums. This allows you to identify the best value for your specific needs.
- Review your business’s risk profile: Analyze your business operations to identify potential risks and assess their likelihood. This information can help you tailor your insurance coverage and potentially negotiate lower premiums.
- Consider bundling policies: Combining multiple insurance policies, such as property and liability insurance, with the same provider can often lead to discounts.
- Be prepared to justify your requests: When negotiating, provide clear reasons for your desired coverage and premium adjustments. This can strengthen your position and increase your chances of success.
Filing and Navigating Insurance Claims
When you need to file an insurance claim, it’s essential to understand the process and follow the necessary steps. Here’s a general Artikel:
- Report the claim promptly: Contact your insurance provider immediately after an incident occurs. The sooner you report the claim, the faster the process can begin.
- Gather documentation: Collect all relevant documentation, such as police reports, invoices, and photos of the damage. This evidence will support your claim and facilitate a smooth process.
- Follow your insurer’s instructions: Each insurer has specific procedures for filing claims. Ensure you adhere to their guidelines and provide all required information.
- Be patient and persistent: The claims process can take time. Stay patient and proactive in following up with your insurer to ensure your claim is progressing.
The Impact of Industry-Specific Insurance Needs
Small businesses operate in diverse industries, each with unique risks and challenges. Understanding these industry-specific needs is crucial for securing adequate insurance coverage. Tailoring insurance policies to the specific risks of an industry helps businesses mitigate potential financial losses and protect their operations.
Industry-Specific Insurance Requirements
Different industries face distinct risks that necessitate specific insurance coverage. Here’s a table outlining some industries and their insurance requirements:
| Industry | Specific Insurance Requirements |
|---|---|
| Construction | Workers’ compensation, general liability, property insurance, builder’s risk insurance, surety bonds |
| Healthcare | Medical malpractice insurance, general liability, property insurance, cyber liability insurance |
| Technology | Cyber liability insurance, errors and omissions insurance, general liability, professional liability insurance |
| Retail | General liability, property insurance, product liability insurance, workers’ compensation |
| Restaurant | General liability, property insurance, liquor liability insurance, workers’ compensation |
| Manufacturing | General liability, property insurance, product liability insurance, workers’ compensation |
Addressing Industry-Specific Risks
Insurance plays a vital role in mitigating the unique challenges faced by each industry. Let’s examine how insurance can address these risks:
- Construction: Construction projects involve inherent risks such as accidents, injuries, property damage, and delays. Workers’ compensation insurance protects employees from financial hardship in case of work-related injuries. General liability insurance covers third-party claims for bodily injury or property damage. Builder’s risk insurance safeguards against damage to the project during construction. Surety bonds guarantee the completion of the project and provide financial protection against contractor defaults.
- Healthcare: Healthcare providers face risks associated with medical errors, patient injuries, and lawsuits. Medical malpractice insurance protects against financial losses arising from claims of negligence or malpractice. General liability insurance covers non-medical claims such as slip-and-falls or property damage. Property insurance safeguards against damage to the healthcare facility. Cyber liability insurance protects against data breaches and cyberattacks, which are increasingly prevalent in the healthcare industry.
- Technology: Technology companies are susceptible to cyberattacks, data breaches, and software errors. Cyber liability insurance provides coverage for financial losses, legal expenses, and regulatory fines resulting from cyber incidents. Errors and omissions insurance protects against claims arising from professional negligence or mistakes. General liability insurance covers non-technology-related claims, while professional liability insurance safeguards against claims arising from professional services rendered.
Examples of Industry-Specific Insurance Policies
Several insurance policies are specifically designed to meet the unique needs of different industries. Here are some examples:
- Builder’s Risk Insurance: This policy provides coverage for damage to a construction project during the building process. It covers risks such as fire, theft, vandalism, and natural disasters.
- Medical Malpractice Insurance: This policy protects healthcare providers against claims of negligence or malpractice. It covers legal defense costs, settlements, and judgments.
- Cyber Liability Insurance: This policy safeguards businesses against financial losses resulting from cyberattacks, data breaches, and privacy violations. It covers costs such as data recovery, legal expenses, and regulatory fines.
- Product Liability Insurance: This policy protects manufacturers and retailers against claims arising from defective products. It covers legal defense costs, settlements, and judgments.
- Liquor Liability Insurance: This policy protects businesses that serve alcohol against claims arising from alcohol-related incidents. It covers legal defense costs, settlements, and judgments.
Future Trends in Small Business Insurance
The small business insurance landscape is undergoing a rapid transformation, driven by advancements in technology and evolving customer expectations. Insurance companies are leveraging innovative solutions to improve efficiency, personalize offerings, and enhance the overall customer experience.
Impact of Technology on Insurance
Technology is revolutionizing the way small businesses access and manage insurance. Online platforms are becoming increasingly popular, offering a streamlined and convenient way to obtain quotes, purchase policies, and manage claims. These platforms often feature user-friendly interfaces, comprehensive coverage options, and real-time policy updates.
- Data-Driven Risk Assessment: Insurance companies are utilizing data analytics to assess risk more accurately and personalize pricing. This involves analyzing factors such as business type, location, past claims history, and even social media activity to create tailored risk profiles.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are being integrated into various aspects of insurance, including pricing, claims processing, and fraud detection. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict future risks, leading to more accurate pricing and efficient claims handling.
The Role of AI and ML in Insurance
AI and ML are poised to transform the insurance industry, impacting both pricing and claims processing. AI algorithms can analyze data from various sources, including historical claims data, market trends, and external data sources, to generate more accurate risk assessments and pricing models. This can lead to more personalized and equitable pricing for small businesses.
- Automated Claims Processing: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are being used to handle routine claims inquiries and process simple claims more efficiently. This can significantly reduce the time and effort involved in claims handling, improving the customer experience.
- Fraud Detection: AI algorithms can identify patterns and anomalies in claims data that may indicate fraudulent activity. This can help insurance companies prevent fraud and reduce unnecessary claims costs.
Future Challenges and Opportunities
The future of small business insurance presents both challenges and opportunities. As technology continues to advance, insurance companies will need to adapt and innovate to stay competitive.
- Data Security and Privacy: As insurance companies collect and analyze more data, ensuring data security and privacy will be crucial. Regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) are increasing the importance of data protection.
- Cybersecurity: Cyberattacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated, posing a significant risk to insurance companies and their clients. Strong cybersecurity measures will be essential to protect sensitive data and maintain customer trust.
- Meeting Evolving Customer Needs: Small businesses are demanding more personalized and flexible insurance solutions. Insurance companies will need to offer customized coverage options and innovative products to meet these evolving needs.
- Increased Competition: The small business insurance market is becoming increasingly competitive, with new players entering the market and traditional insurers innovating to stay ahead.
Last Recap
Securing the right insurance for your small business is a proactive step toward safeguarding your future. By understanding the various coverage options, choosing a reliable provider, and implementing risk management practices, you can build a strong foundation for success. Remember, a comprehensive insurance strategy is an investment in your business’s long-term stability and growth. This guide provides a starting point, and consulting with an insurance professional is recommended to ensure your specific needs are met.