Life insurance cost is a crucial aspect of financial planning, and understanding its intricacies is essential for making informed decisions. This guide delves into the factors influencing life insurance premiums, providing insights into how age, health, lifestyle, coverage amount, and policy type impact the cost. We’ll explore strategies for saving on life insurance, including tips for finding affordable options, comparing quotes, and negotiating with agents. Additionally, we’ll examine the importance of conducting a life insurance needs assessment to determine appropriate coverage levels based on individual circumstances.
This comprehensive guide covers various aspects of life insurance cost, including policy features, specific needs considerations, industry trends, and valuable resources. Whether you’re seeking to protect your loved ones from financial hardship or ensure your business continuity, understanding life insurance cost is paramount. By navigating the complexities of life insurance premiums, you can make informed decisions that align with your financial goals and provide peace of mind.
Understanding Life Insurance Quotes
A life insurance quote is a personalized estimate of the cost of your policy. It reflects your individual circumstances, such as your age, health, and the amount of coverage you need. It is crucial to understand the components of a life insurance quote to make informed decisions about your coverage.
Components of a Life Insurance Quote
Here are the key components that typically make up a life insurance quote:
- Death Benefit: This is the amount of money your beneficiaries will receive upon your death. It’s the core of your life insurance policy.
- Premium: This is the amount you pay periodically (monthly, annually, etc.) for your life insurance policy. It’s the price of your coverage.
- Policy Term: This refers to the duration of your life insurance policy. It can be a specific period (e.g., 10 years, 20 years) or a lifetime policy.
- Age and Health: These factors heavily influence the cost of your life insurance. Younger and healthier individuals generally pay lower premiums.
- Lifestyle and Habits: Your lifestyle choices, such as smoking or engaging in risky activities, can impact your premium.
- Coverage Type: Different types of life insurance policies, such as term life or whole life, have varying costs.
- Riders: Additional features or benefits you can add to your policy, such as accidental death benefit or critical illness coverage, may increase your premium.
Common Terms and Definitions Used in Quotes
- Face Value: The death benefit amount stated in your life insurance policy.
- Premium Payment Frequency: How often you choose to pay your premium (e.g., monthly, quarterly, annually). This can affect the overall cost of your policy.
- Cash Value: This is a feature found in some life insurance policies, such as whole life policies. It refers to the savings component that accumulates over time, which you can access or borrow against.
- Guaranteed Insurability: This option allows you to purchase additional coverage at specific intervals without requiring a medical exam, even if your health changes.
- Waiver of Premium: This rider protects your policy if you become disabled. It ensures your premiums are paid even if you can’t work.
Premium Payment Frequency
The frequency at which you pay your premiums can influence the total cost of your life insurance.
- Paying more frequently (e.g., monthly) often results in a slightly higher overall cost due to interest charges. However, it can be more manageable for your budget.
- Paying less frequently (e.g., annually) can be cheaper because you avoid interest charges. However, it requires a larger lump-sum payment.
Cash Value in Life Insurance
Cash value is a savings component that builds up within some life insurance policies, particularly whole life policies.
- Benefits:
- Accumulates over time: Cash value grows over time, potentially offering a return on your investment.
- Tax-deferred growth: The earnings on your cash value are generally not taxed until you withdraw them.
- Borrowing options: You can borrow against your cash value for various needs, such as education or home improvements.
- Limitations:
- Lower death benefit: Compared to term life insurance, whole life policies typically have a lower death benefit for the same premium.
- Higher premiums: Whole life policies generally have higher premiums than term life policies due to the cash value component.
- Investment risk: Cash value growth is not guaranteed and can fluctuate based on market performance.
Different Quote Options
Life insurance companies offer various quote options to cater to different needs and budgets.
- Term Life Insurance: Provides coverage for a specific period (e.g., 10, 20, 30 years). It’s typically more affordable than permanent life insurance but doesn’t accumulate cash value.
- Whole Life Insurance: Offers lifetime coverage and accumulates cash value. It’s generally more expensive than term life insurance but provides long-term financial security.
- Universal Life Insurance: Combines features of term and whole life insurance, offering flexibility in premium payments and death benefit amounts. It also accumulates cash value.
- Variable Life Insurance: Allows you to invest your premiums in sub-accounts that can potentially grow faster than traditional whole life insurance. However, it also carries investment risk.
Life Insurance Needs Assessment: Life Insurance Cost
Determining the right amount of life insurance is crucial for ensuring your loved ones’ financial security in the event of your passing. A life insurance needs assessment helps you calculate the coverage required to meet your family’s financial obligations and maintain their lifestyle.
Understanding the Importance of a Needs Assessment
A life insurance needs assessment is a comprehensive analysis that helps you determine the appropriate amount of coverage based on your individual circumstances. It considers your current financial situation, future financial goals, and the potential financial impact of your death on your dependents. Conducting a needs assessment provides valuable insights into your coverage needs and ensures that your family is adequately protected in the event of your passing.
Steps to Determine Coverage Requirements
To conduct a life insurance needs assessment, follow these steps:
- Calculate your outstanding debts: This includes mortgage loans, credit card debt, student loans, and any other outstanding financial obligations.
- Estimate your dependents’ living expenses: Determine the annual cost of living for your spouse and children, including housing, food, transportation, healthcare, education, and other essential expenses.
- Consider your dependents’ future needs: Include expenses like college education, retirement, and other long-term financial goals that your dependents may have.
- Account for income replacement: Estimate the amount of income your dependents will need to replace your lost earnings. This can be calculated by considering your current income and the time remaining until your dependents become financially independent.
- Factor in special expenses: Include any significant expenses, such as funeral costs, estate taxes, or charitable donations, that your family may need to cover after your passing.
Evaluating Financial Obligations
When evaluating your financial obligations, consider the following factors:
- Mortgage: The outstanding balance on your mortgage is a significant financial obligation that your family will need to address.
- Other debts: Include any other debts, such as credit card debt, student loans, or car loans, in your assessment.
- Living expenses: Calculate the cost of living for your dependents, including housing, food, transportation, healthcare, and other essential expenses.
- Future needs: Consider your dependents’ future needs, such as college education, retirement, or other long-term financial goals.
- Income replacement: Estimate the amount of income your dependents will need to replace your lost earnings.
Resources for Calculating Life Insurance Needs
Several online calculators and resources can help you determine your life insurance needs. These tools often ask for information about your income, dependents, debts, and other financial obligations to provide an estimated coverage amount.
Example: Many financial institutions, insurance companies, and independent websites offer free online life insurance needs calculators.
Checklist of Key Considerations for Individual Circumstances
When conducting a life insurance needs assessment, consider the following factors specific to your individual circumstances:
- Age and health: Your age and health status can significantly impact your life insurance premiums.
- Family size and dependents: The number and age of your dependents will determine the amount of coverage needed.
- Financial goals: Your financial goals, such as retirement planning or college savings, can influence your life insurance needs.
- Income and expenses: Your current income and expenses will help determine the amount of income replacement needed for your dependents.
- Estate planning: Your estate planning strategies, such as trusts or wills, can affect your life insurance needs.
Life Insurance for Specific Needs
Life insurance isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. The right policy depends on your individual circumstances, goals, and needs. Let’s explore some key situations where life insurance plays a crucial role.
Life Insurance for Families
Life insurance is essential for families, providing financial security in the event of the unexpected. It acts as a safety net, ensuring loved ones can maintain their lifestyle, pay off debts, and cover living expenses without financial strain.
- Financial Support for Dependents: A life insurance policy can provide a lump-sum payout to cover essential expenses for surviving family members, such as mortgage payments, childcare, education costs, and living expenses.
- Debt Coverage: Life insurance can be used to pay off outstanding debts, such as mortgages, loans, and credit card balances, relieving financial pressure on the family.
- Income Replacement: For families relying on a single income, life insurance can help replace lost earnings, ensuring financial stability for surviving spouses and children.
Life Insurance for Business Owners
Life insurance plays a vital role in protecting businesses and ensuring their continuity. It safeguards against the financial repercussions of the death of a key employee or business owner.
- Business Continuity: Life insurance can provide funds to cover the costs of replacing a key employee or business owner, ensuring smooth operations and minimizing disruption.
- Debt Repayment: Life insurance can be used to pay off business debts, protecting the company’s financial stability in the event of a loss.
- Buy-Sell Agreements: Life insurance can be used to fund buy-sell agreements, ensuring a smooth transition of ownership in the event of the death of a partner or shareholder.
Life Insurance for Individuals with Dependents
Life insurance is particularly important for individuals with dependents, providing financial security for their loved ones in the event of their passing.
- Childcare and Education: Life insurance can provide funds for childcare, education expenses, and other needs of children, ensuring their financial well-being.
- Financial Stability: Life insurance can help maintain the family’s financial stability, allowing surviving spouses to cover living expenses, mortgage payments, and other necessities.
- Debt Coverage: Life insurance can be used to pay off debts, such as mortgages, student loans, and credit card balances, relieving financial pressure on the family.
Life Insurance in Estate Planning
Life insurance plays a crucial role in estate planning, helping to ensure the smooth transfer of assets and minimize tax burdens.
- Estate Liquidity: Life insurance can provide liquidity to the estate, allowing for the payment of taxes, debts, and other expenses without having to sell assets.
- Tax Minimization: Life insurance proceeds are generally exempt from income tax, reducing the overall tax burden on the estate.
- Asset Distribution: Life insurance can be used to ensure the distribution of assets according to the deceased’s wishes, providing financial security for beneficiaries.
Life Insurance Products Tailored to Specific Situations, Life insurance cost
Life insurance policies are available to address specific needs and situations, offering tailored solutions for individuals and families.
- Term Life Insurance: Provides coverage for a specific period, typically 10 to 30 years. It is an affordable option for individuals with temporary needs, such as covering a mortgage or providing income replacement.
- Whole Life Insurance: Offers lifelong coverage and builds cash value, providing both death benefit and savings component. It is suitable for long-term financial planning and estate planning purposes.
- Universal Life Insurance: Combines death benefit with a flexible savings component, allowing policyholders to adjust premiums and death benefit amounts. It offers greater flexibility and customization options.
- Variable Life Insurance: Offers death benefit and investment options, allowing policyholders to invest premiums in a variety of sub-accounts. It provides potential for higher returns but also carries higher risk.
- Indexed Universal Life Insurance: Combines death benefit with a savings component linked to the performance of a specific index, such as the S&P 500. It offers potential for growth while providing downside protection.
Life Insurance Resources and Information
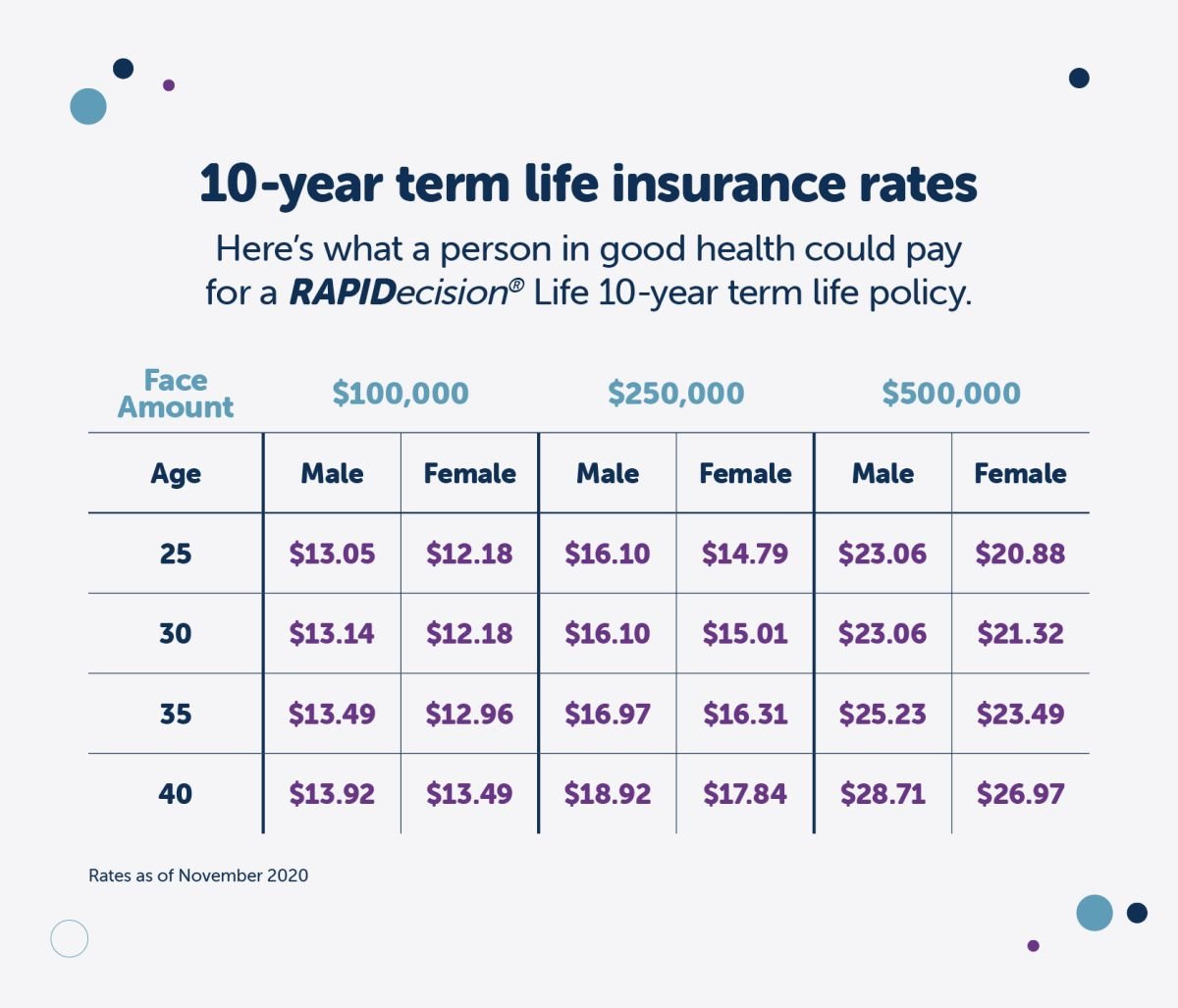
Navigating the world of life insurance can feel overwhelming, especially with the wide range of options and complex terms. Luckily, there are many resources available to help you make informed decisions and ensure you’re getting the coverage you need.
Trusted Organizations and Resources
This section provides a list of reputable organizations and resources that offer valuable information and guidance on life insurance.
- National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC): The NAIC is a non-profit organization that serves as a resource for state insurance regulators and consumers. It provides information on life insurance policies, consumer rights, and complaint resolution processes. https://www.naic.org/
- Consumer Reports: Consumer Reports is a well-respected independent organization that provides unbiased reviews and ratings of various products and services, including life insurance. https://www.consumerreports.org/
- National Endowment for Financial Education (NEFE): NEFE is a non-profit organization dedicated to promoting financial literacy. They offer educational materials and resources on life insurance and other financial planning topics. https://www.nefe.org/
- The Life Insurance Marketing and Research Association (LIMRA): LIMRA is a non-profit organization that provides research and data on the life insurance industry. They offer insights into trends and best practices in life insurance. https://www.limra.com/
- The American Council of Life Insurers (ACLI): ACLI is a trade association representing life insurance companies. They provide information on life insurance products and services, as well as consumer protection resources. https://www.acli.com/
Government Websites and Consumer Protection Agencies
Government websites and consumer protection agencies play a crucial role in protecting consumers and ensuring fair insurance practices. Here are some important resources:
- Federal Trade Commission (FTC): The FTC is a federal agency that protects consumers from unfair and deceptive business practices. They provide information on life insurance scams and how to avoid them. https://www.ftc.gov/
- Your State Insurance Department: Each state has its own insurance department that regulates insurance companies and protects consumers. You can find contact information for your state’s insurance department on the NAIC website. https://www.naic.org/
- Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB): The CFPB is a federal agency that protects consumers in the financial marketplace. They provide information on life insurance products and services, as well as complaint resolution processes. https://www.consumerfinance.gov/
Choosing a Reputable Insurance Agent or Broker
Choosing the right insurance agent or broker is essential for finding the best life insurance policy for your needs. Here are some tips for selecting a reputable professional:
- Check Their Credentials: Ensure the agent or broker is licensed and in good standing with your state’s insurance department. You can verify their credentials on the NAIC website. https://www.naic.org/
- Seek Recommendations: Ask friends, family, or financial advisors for recommendations.
- Interview Multiple Agents: Don’t settle for the first agent you meet. Interview several agents to compare their expertise, experience, and approach.
- Look for a Fiduciary: A fiduciary is legally obligated to act in your best interest.
- Check for Conflicts of Interest: Ensure the agent or broker is not representing multiple insurance companies that may have conflicting interests.
Reading Policy Documents Carefully
Life insurance policies are complex legal documents. It’s crucial to read and understand the terms and conditions before you sign anything.
- Understand the Coverage: Carefully review the policy’s coverage details, including the death benefit amount, the beneficiary information, and the exclusions or limitations.
- Review the Premiums: Make sure you understand the premium amount, the payment schedule, and any potential premium increases.
- Consider the Policy Term: Understand the policy’s term length and whether it’s a permanent or temporary policy.
- Ask for Clarification: Don’t hesitate to ask your agent or broker to clarify any confusing terms or conditions.
Filing a Complaint Against an Insurance Company
If you have a complaint about an insurance company, you should first attempt to resolve the issue directly with the company. If you are unable to reach a resolution, you can file a complaint with your state’s insurance department.
- Gather Documentation: Keep detailed records of all your communications with the insurance company, including dates, times, and the names of the people you spoke with.
- File a Complaint: Contact your state’s insurance department and file a formal complaint.
- Follow Up: Follow up with the insurance department to check on the status of your complaint.
Conclusion
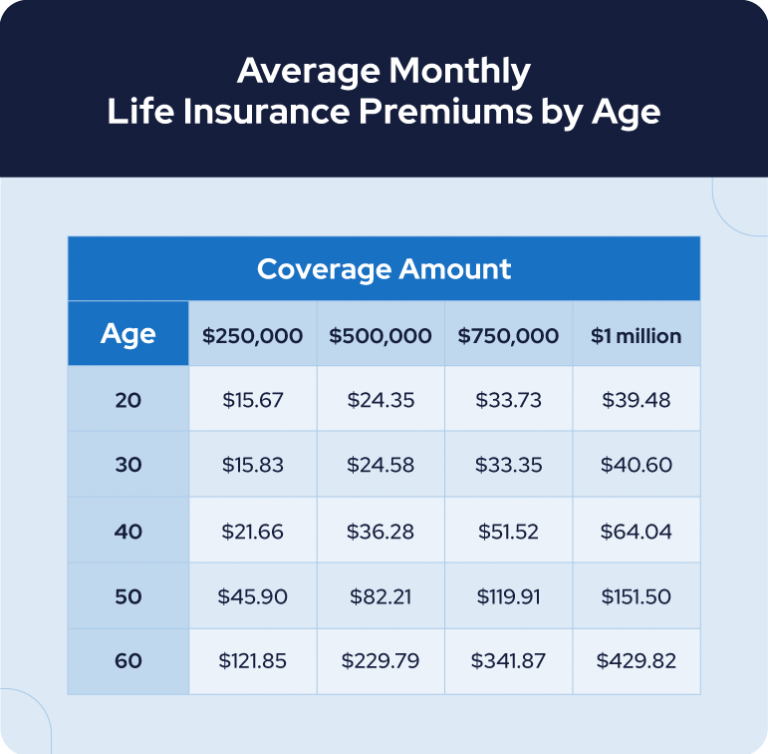
In conclusion, understanding life insurance cost is a crucial step towards securing your financial future and protecting your loved ones. By carefully considering the factors influencing premiums, exploring strategies for saving, and conducting a needs assessment, you can obtain the right coverage at a price that fits your budget. Remember, life insurance is an investment in your peace of mind, ensuring that your loved ones are financially secure in the event of your absence. By embracing the insights and strategies presented in this guide, you can navigate the complexities of life insurance cost and make informed decisions that provide lasting financial protection.
The cost of life insurance can vary greatly depending on factors like age, health, and coverage amount. It’s also important to consider the cost of family health insurance as a crucial component of your overall financial planning. While life insurance protects your loved ones in the event of your passing, health insurance safeguards your family’s well-being in the face of medical emergencies, helping to manage the costs associated with healthcare.
